Does maternal immunity in rabbits protect the animal against RHD?
The simple answer to this question is yes, maternal immunity based on the transfer of IgG from female rabbits to their offspring protects them against rabbit haemorrhagic disease . However, other questions may then come up, such as how long this protection lasts or by what means these antibodies are transmitted.
In 2020, the study "Characterization of the Maternally Derived Antibody Immunity against Rhdv-2 after Administration in Breeding Does of an Inactivated Vaccine”, which attempted to answer these questions, was published in the journal Vaccines.
The study design consisted of serological monitoring of two groups of female rabbits, one vaccinated and the other unvaccinated, and their progeny.
Route Of Transmission Of Maternal Immunity
It was demonstrated in this study that the main route of transmission of IgG antibodies to rabbit kits is through pregnancy. To demonstrate this, it was necessary to carry out different types of breeding, as shown in Table 1. In this way, through the serology of the kits, it was possible to differentiate the route by which IgG antibodies are transmitted.
| Group AA | Group AB | Group BA | Group BB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pregnancy in vaccinated does | X | X |
|
|
| Pregnancy in unvaccinated does |
|
| X | X |
| Lactation in vaccinated does | X |
| X |
|
| Lactation in unvaccinated does |
| X |
| X |
Graph 1 shows the serology of the kits belonging to each group. Kits from vaccinated mothers had a similar seropositivity, which was higher in those that were also nursed by vaccinated mothers. In the case of kits from unvaccinated mothers, the serological impact of being nursed by vaccinated mothers did not mean in any case that the animals were seropositive. Thanks to these results, it was possible to demonstrate that the main route of transmission is through pregnancy and that lactation did not have a significant impact on the IgG levels of the kits.
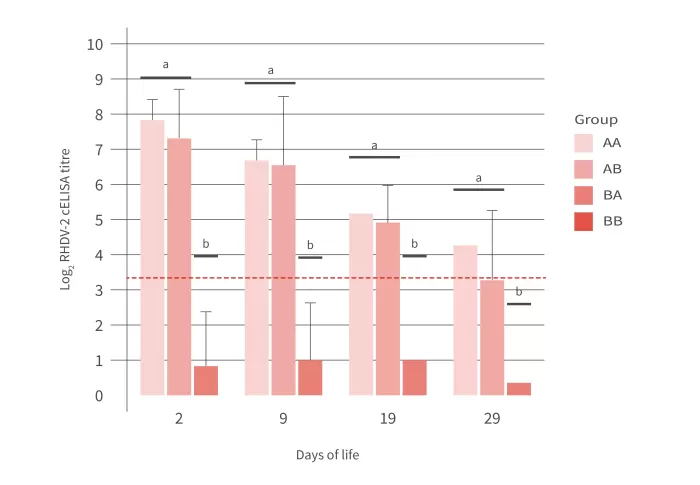
Graph 1: Serology against RHDV2 of the offspring of does from the different groups.
Duration Of Maternal Immunity
Now that we are clear about the main route of transmission, we would have to answer the second big question, which is: until when is this IgG-based maternal immunity present in the rabbits' offspring?
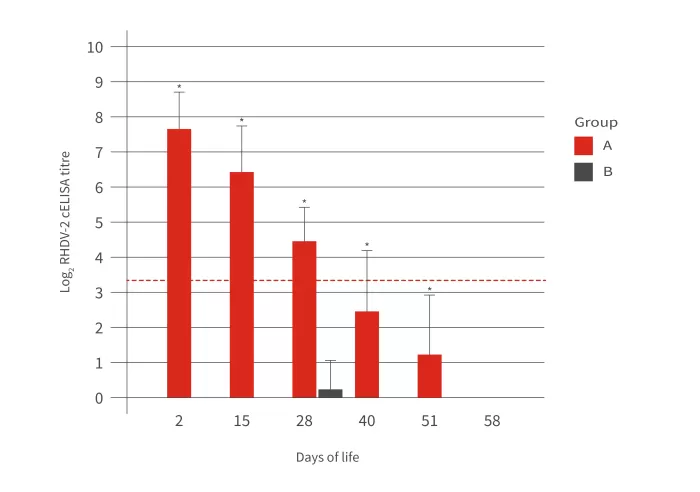
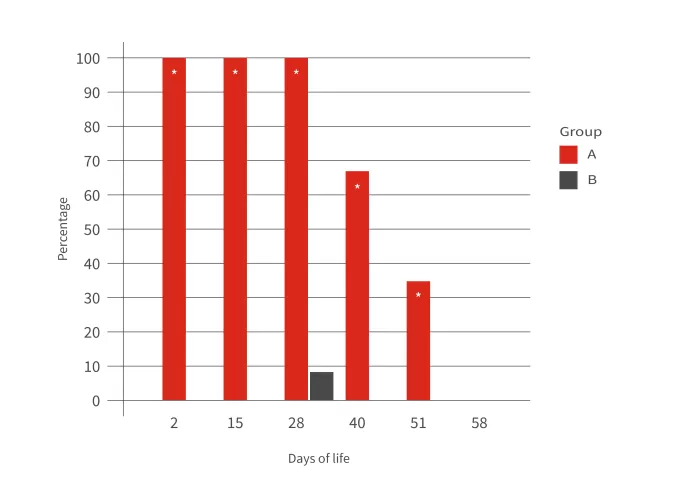
Graph 2: Serology against RHDV2 of rabbit offspring from 2 days old to 58 days old. Graph A shows the mean antibody titres. Graph B shows the percentage of seropositive animals.
Within this same study, serological monitoring of the kits was carried out from the age of 2 days to 58 days. Graph 2 shows how all the animals maintained maternal immunity until the age of 28 days. However, there is a tendency for the mean antibody titres to progressively decrease. So, at 40 days old, approximately 30% of the animals were seronegative. Therefore, these animals would then be susceptible to suffering from the disease.
Thus, when pregnant rabbits are adequately vaccinated, it is reasonable to expect that the kits will be protected during their first 28 days of life. However, it is evident that this maternal immunity will progressively decrease until it reaches levels insufficient to counteract an RHD infection. It is therefore essential to implement a preventive strategy to avoid contagion, as well as to vaccinate rabbits at an early age to protect them from RHD.
References
Baratelli M, Molist-Badiola J, Puigredon-Fontanet A, Pascual M, Boix O, Mora-Igual FX, Woodward M, Lavazza A, Capucci L. Characterization of the Maternally Derived Antibody Immunity against Rhdv-2 after Administration in Breeding Does of an Inactivated Vaccine. Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Aug 28;8(3):484. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8030484. PMID: 32872139; PMCID: PMC7564433.
